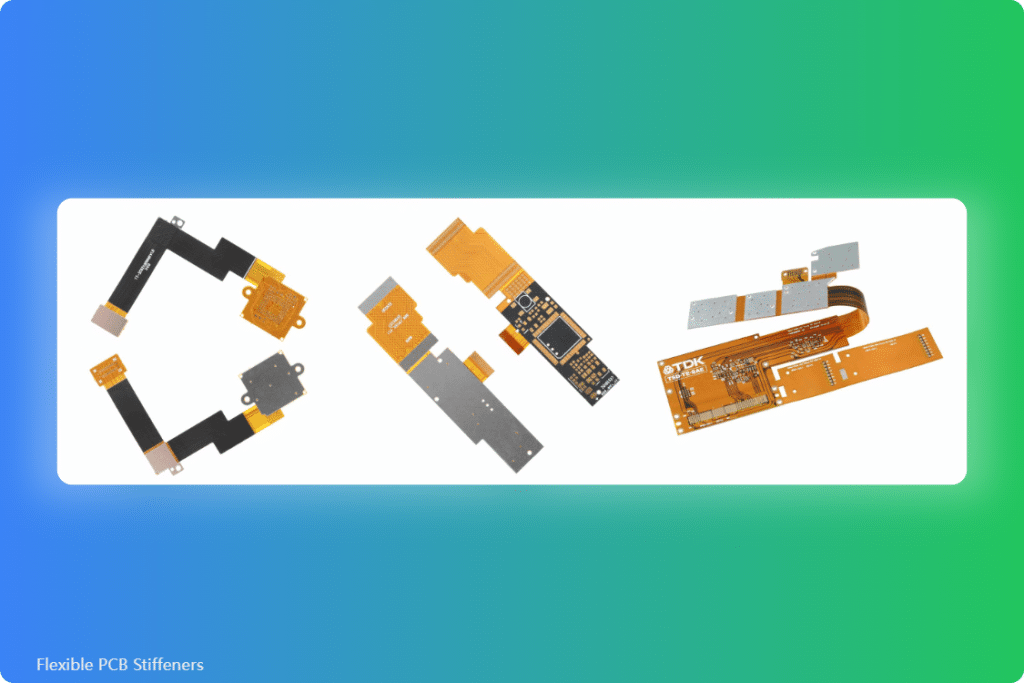
Flexible Printed Circuit Boards are among the most common types of PCBs. Flexible PCBs are very useful in several electronic applications as they facilitate the design of products with circuitry where a rigid PCB design is unsuitable. However, in situations where stiffness is required alongside the adaptability of a flexible PCB, the flexibility of a flex PCB may be a drawback, hence the need for Flexible PCB Stiffeners. Flexible PCB stiffeners help improve flexible circuits’ reliability and durability in various applications.
This article will discuss the following to help you understand flexible PCB stiffeners.
- What are flexible PCB stiffeners?
- What is the Stiffener Material?
- Why Does Your Flexible And Rigid-flex PCB Need Stiffener?
- What is the thickness of the flexible PCB stiffener?
- What are flexible PCB stiffeners used for?
- When are stiffeners required in flexible PCBs?
- Why Use Stiffeners in Flexible Circuit Applications
- Can PCB Stiffeners Improve The Performance Of The PCB?
- How To Apply PCB Stiffeners On Flex PCBs?
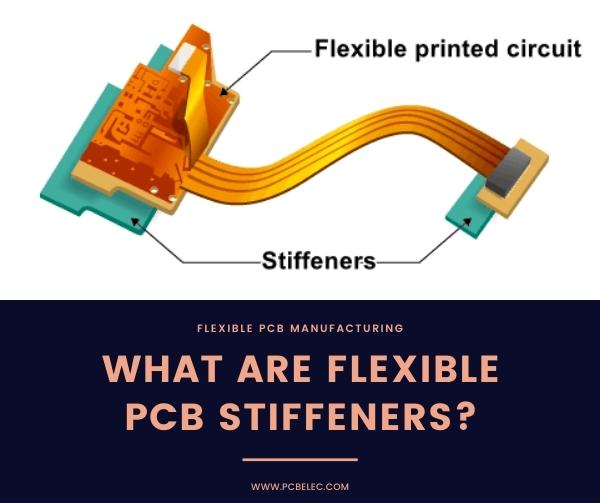
Flexible Printed Circuit Board stiffeners are applied to make certain parts of a flexible PCB rigid or stiff in order to make it easier for components to be soldered to the harder or stiffer part of the Board. Flexible PCB stiffeners are not part of a PCB’s electrical circuitry. Flex PCB stiffeners are applied simply to provide support mechanically to the flexible PCB during the process of assembly of the flex PCB. In addition, the stiffeners also improve the abrasive resistance of the PCB which reinforces the soldered joints and makes the PCB to be appropriately handled during the automation process of picking and placing the finished PCBs.
There are three major types of Printed Circuit Board stiffeners namely FR-4 stiffener, PI (Polyamide) stiffener, and stainless steel/aluminum stiffener. These stiffeners are commonly used in projects that require enhanced stiffness and greater heat dissipation.
Polyimide (PI) is an organic polymer special engineering material with the best all-around performance. It is widely used in aviation, aerospace, microelectronics, nanometer, liquid crystal, separation film, laser, and other fields; it has the advantages of high insulation, excellent mechanical properties, high and low-temperature resistance, and dielectric loss of only 0.004-0.007.
PI (polyimide) stiffener is usually used to connect to ZIF connectors. PI Stiffener is used in the area on the back of the FPC golden finger. The thickness of the PI stiffener is mainly selected according to the design drawings and the use environment.
Compared with FR-4 and PI stiffener, the use of stainless steel or aluminum as the stiffener material of the flexible PCB will increase the production cost of the flexible PCB. Aluminum is a material with good heat dissipation properties. Therefore, using aluminum as a stiffener material usually requires heat dissipation applications. When the crimping stiffener has insufficient space, stainless steel is usually used as the stiffener material for the flexible PCB.
Stainless steel stiffener usually uses 303 stainless steel.
Flex PCBs can easily bend as they are made of a flexible material, such as Polyimide. They can easily bend according to the available space. But this bending is not always required; sometimes, it is quite harmful to the PCB and can damage the circuit.
Flexible PCBs are so flexible that sometimes there is a need for rigidity at some places. For instance, if a certain part of the flexible PCB bends too much, there is a need for a flex PCB stiffener to strengthen that part. Otherwise, the flexible PCB won’t last as it should.
If there is a high density of components required on a flex PCB, then either that part is made of a rigid substance, making the PCB rigid-flex, or stiffeners are used to prevent any damage to the components and offer optimal life span to the board. Components have a certain weight that flexible PCBs cannot handle alone. But thanks to the PCB stiffeners for allowing high-density of components on flexible circuits.
SMDs and specifically through-hole components require a rigid board. Flexible circuits cannot accommodate these components for a long time without enough support. Therefore, stiffeners are specially used for this purpose.
Often there are connectors on the flexible PCBs. These connectors need support or a rigid piece underneath. Stiffeners are used to offer support to these connectors.
If a certain area of the PCB requires more thickness, stiffeners can increase the thickness without any hassle. After the manufacturing of the circuit, stiffeners can be applied.
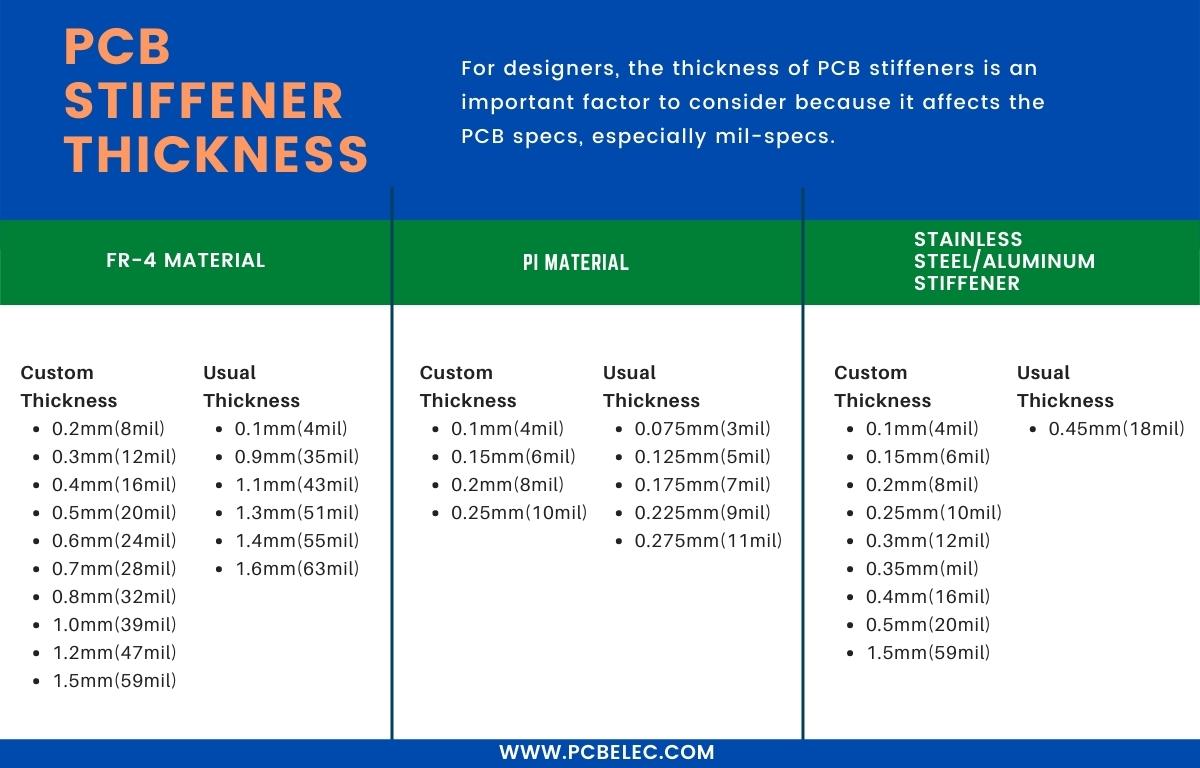
The thickness of the flexible circuit board is skinny. For PCB designers, the thickness of the PCB stiffener is also an essential factor that cannot be ignored because it will also affect the specifications of the flexible PCB, especially in military and aerospace applications.
- FR-4 Stiffener Thickness:0.003″(0.08mm)-0.125 “(3.18mm);
- PI Stiffener Thickness: 0.001″ (25μm), 0.002″ (50μm), 0.003″ (75μm) and 0.005″ (125μm) are available;
- Stainless steel/aluminum stiffeners Thickness: 0.1mm (4mil) – 0.45mm (18mil).
Some thickness measurements are readily available, but you can also go for custom thickness. The only thing that should be considered is uniformity; the thickness should be uniform throughout the circuit.
A flexible PCB stiffener is used to harden a particular part of a flexible PCB. Please note that a PCB stiffener is not an essential component of an electrical PCB design. A PCB stiffener applied to a flexible PCB will prevent a flexible circuit from getting bent or twisted and protect the quality and integrity of the soldered joint. Below are some reasons why flexible PCB stiffeners are used:

- Flexible PCB stiffeners provide mechanical support to specific parts of the flexible PCB that has Surface Mount Technology (SMT) and/or Plated-Through Holes (PTH) components.
- Flexible PCB stiffeners maintain the appropriate thickness in flexible circuits.
- A Flex PCB stiffener supports PCB connects and components
- As required, flex PCB stiffeners help to restrict the flexible sections of the flex PCB to the hardened part of the flexible PCB.
- The stiffeners used in flexible PCB facilitate better handling and treatment of a flexible circuit board during the automated reflow and pick-and processes.
- Flexible PCB stiffeners keep the stiffener parts of the flexible circuits stable and flat.
- The stiffeners help the flexible PCB meet the specifications of ZIF (Zero Insertion Force) connectors.
- The application of a flexible PCB stiffener increases the bending radius of a flexible circuit at the intersecting point of the flexible and stiff part of the circuit board. This helps to prevent stress on the flexible part of the circuit during multiple bends or twists.
- Flexible PCB stiffeners help to route and maintain the array of flex PCBs. This is made possible by extending the FR-4 stiffener material into the flexible PCB array.
As earlier mentioned, PCB stiffeners are required and commonly used in several designs and applications to improve the reliability and durability of flexible and rigid-flexible PCBs. A PCB stiffener like FR-4 for flexible PCBs is required when:

- Components are mounted on a flexible part of the circuit board.
- The weight or mass of components mounted on the flexible part of the circuit board stresses the flexible material.
- There is need to create a hard and flat surface on the flexible PCB for mounting SMT pad components.
- Connection that need multiple insertions required a PCB stiffener to minimize the pads’ stress.
- Mounting PTH components. It is recommended that the stiffener is placed on the side of the flexible PCB where the PTH components are placed to enable the solder pads to be accessed directly. In some situations, the manufacture wants to be economical during the final stage of the project assembly. For the manufacturer to achieve this, a flexible PCB stiffener is added on the flexible PCB panel (around the border) to replace the Surface Mount Technology carrier completely.
Flexible PCB stiffeners are required under the following categories:
- Hardening areas where components/connectors are placed.
- Zero Insertion Force (ZIF) Thickness Requirements
- Restricted Bends
Components / Connectors Stiffeners
Functions:
- Creates a restricted hard region where connectors or components are mounted.
- Prevents the twisting of the flex around the components area thereby protecting the soldered joints.
Material Options:
- FR4, Aluminum, Polyimide, Stainless Steel
- Various thicknesses are available
- Mounting methods:
- Bonded thermally using flex adhesives
- Pressure Sensitive Adhesive (PSA)
ZIF PCB Stiffeners
Function(s):
- Local thickness increases at the contact fingers in order to meet the specific ZIF connectors’ specifications or requirements.
Material Options:
- Only Polyimide
- Various thicknesses are available in order to meet the specific design specifications.
- Attachment methods:
- Bonded thermally with only flex adhesives
Restricted Bends
Function(s):
- Restrict the bend areas) to a specific area(s) in a flex design to aid the final assembly, attain specific bend specification(s) or other end-users requirements.
Material Options:
- Polyimide, FR4
- Various thicknesses are available
- Methods of attachment:
- Thermally Bonded using flex adhesives
- Pressure Sensitive Adhesive (PSA)
- What is the thickness of the flexible PCB stiffener?
Yes, the performance of flexible PCBs can be significantly improved by using stiffeners. Flexible PCBs are flimsy and can fail due to a bit of strain. Therefore, it is necessary to keep the strain away from the PCBs.
Stiffeners offer the support that flex PCBs need. It provides rigid support to the components and area where it is applied. It ensures the reliability of the PCB and its performance.
There are two main methods for applying PCB stiffeners on the board.
Pressure Sensitive Adhesives
It is the simplest method of applying flex PCB stiffeners. You only need to apply a little pressure, and the adhesive will create a bond with the flexible PCB; it is just like you apply stickers. It is simple to do yet does not provide a very strong bonding; the stiffener can be removed when required. It is cheap and quick, and even buyers can do it without help from PCB manufacturers.
Thermal Bonding
Thermal bonding is an advanced yet expensive method of applying PCB stiffeners. The stiffeners are placed on the flexible PCBs, and heat and pressure are applied. It creates a strong bonding with the flexible PCB that it is not possible to remove without damaging the PCB. It is usually used in high-performance devices, such as military equipment and aerospace devices.
Conclusion
Flexible PCB stiffeners, like FR4 are commonly used in flex PCBs when rigid or hard areas are required in flex circuits to protect connectors or components mounted on the flexible PCB and the flex circuit from bending or twisting. This also maintains the integrity and quality of the soldered joints. FR4 materials are attached either with PSA or thermally bonded acrylic adhesives. This serves your requirements of hardening a specific area in a flexible circuit.
Flex PCB stiffeners are neither a part of the PCB nor required in the functioning. Instead, they offer mechanical support that flexible PCBs need. They offer a surface for components, provide rigidity, and make the circuit more reliable. They are often necessary to support the PCB and strengthen it, and without them, flex PCB will fail to deliver the required performance and last for the expected life. However, they do not contribute to the electrical purpose for which PCB is used.
Related Reading
- Knowledge of Flexible Printed Circuit Board Processing Technology
- The terms you have to know related to the manufacture of Flexible PCB
- Complete Introduction of Flexible Circuit Board Materials
- Complete Introduction To Flexible PCB Assembly Process
- What is Flexible PCB Prototype?
- 16 Factors Affecting The Cost And Price of Flexible PCB
- How to Solder On Flex PCB?
- What Are The Advantages And Applications Of Rigid-Flex PCBs?
- What is a PCB Manufacturer? The Definitive Guide
- Custom Flex PCB:Tailored Solutions for Your Applications
- Custom PCB Fabrication in China – Prototyping & Mass Production
- Introduction to Semi-Flex PCBs: Bridging Rigid and Flex PCBs
- Flexible PCB Manufacturing: A Guide to Fabrication and Assembly
- How to Select the Right Flexible PCB Manufacturer for Your Product: A 6-Step Guide
- Layer Stackup in Rigid-Flex PCB
- What Are The Types of Flexible Circuit Boards?
- Flexible PCB Cost: Why It’s More Expensive and How to Reduce It
- What Is Flexible PCB Coverlay (FPC Cover Layer)?
- The Manufacturing Process Of Double-sided Flexible PCB Coverlay