What is FR-4 Material in PCB Fabrication?
- The Guide To Fr-4 Material for Printed Circuit Board
- Is Fr4 The Best Material For Your Design?
Home » PCB Materials » Fr-4 Material
FR-4/FR4, hearing this technical term for the first time might make you perplexed. Even after searching here and there, you might remain confused and clueless because it is a difficult technical term, and many things are involved.
However, you don’t need to be nervous. We are here to guide you and help you understand what it is.
FR-4 is actually a grade of flame-resistant material, meaning that the resin is able to extinguish itself after being burned. If there is an emergency fire, we don’t have to worry about it; it will extinguish itself and won’t spread. FR-4 can effectively suppress the loss and casualties of property and personnel.
Electronic equipment tends to run for a long time, which will inevitably generate a lot of heat. Various heating components generate heat. In order to enable the electronic components and the entire electronic equipment to work safely and effectively, the printed circuit boards of the components must be manufactured with reliable and stable materials.

What is FR-4 or FR4?
FR-4 is a code for the grade of flame-retardant materials, a material standard stipulated by NEMA American Electrical Manufacturers Association. FR-4 means a material specification that the resin material must be able to extinguish itself after being burned. It is not a material name but a material grade.
FR stands for “flame retardant” and indicates that the material meets the UL94V-0 flammability standard for plastic materials.
FR-4 uses bromine; this chemical element becomes a halogen, which has excellent fire resistance.
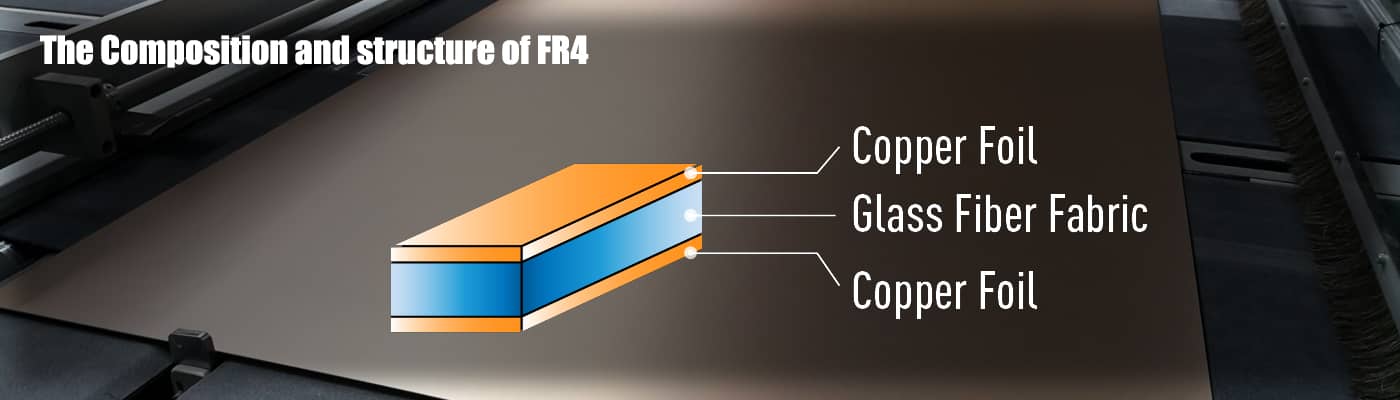
FR-4 epoxy glass fiber cloth substrate is laminated with epoxy resin as adhesive. It has the electronic grade glass fiber cloth as a reinforcing material. One or both sides are covered with copper foil and hot-pressed at high temperature and high pressure. This is a composite board because it is made up of different materials. It is also known as Copper Clad Laminate (CCL) in the electronics manufacturing industry.
FR-4 is an important substrate for making multilayer printed circuit boards. A standard FR-4 PCB consists of an FR-4 layer sandwiched between two thin copper foils.
Printed circuit boards with various functions are selectively processed on copper-clad laminates. To make different printed circuit boards, the board goes through different processes, such as drilling, etching, and copper sinking. The performance, quality, processability, manufacturing cost, reliability, and stability of printed circuit boards depend on the FR4 copper clad laminate to a large extent.
FR-4 is the most widely used product model of Epoxy glass fiber cloth substrate. Due to the development of electronic product mounting technology and PCB technology, FR-4 products with high Tg have are easily available now.
The Performance Characteristics of FR-4 Substrate

The epoxy glass fiber cloth substrate has good mechanical properties, dimensional stability, impact resistance, moisture resistance, and heat resistance. It also has good insulation and dielectric properties. In terms of processing technology, it has great advantages over other resin glass fiber cloth substrates. This type of product is mainly used for double-sided PCB and is quite common in the industry.
- Vertical layer direction bending strength: Normal state — E-1/150, 150±5℃≥340Mpa
- Parallel layer direction impact strength (simple beam method): ≥230 KJ/m
- Insulation resistance after immersion in water (D-24/23): ≥ 5.0×108Ω
- Vertical layer direction electric strength (in 90±2℃ transformer oil, plate thickness 1mm): ≥14.2MV/m
- Parallel layer direction breakdown voltage (in 90±2℃ transformer oil): ≥40KV
- Relative dielectric constant (50Hz): ≤5.5
- Relative permittivity (1MHz): ≤5.5
- Dielectric loss factor (50Hz): ≤0.04
- Dielectric loss factor (1MHz): ≤0.04
- Electrical strength: 800 to 1800volts/mil
- Surface resistivity (ρS) (Ohm /square unit): 105 to 1010
- Water absorption (D-24/23, plate thickness 1.6mm): ≤19mg
- Density: 1.70-1.90g/cm & sup3
- Flammability: FV0
- FR-4 sheet Tg value: Generally, 130 ℃, 140℃, 150℃, 170℃, and 180°
- FR4 high CTI: Tracking index of about 600 volts
FR4 Material Properties of Various Manufacturers
Name | Manufacturer | Glass transition temperature (Tg) | Decomposition temperature (Td) | Dielectric constant @ 10GHz | Dissipation factor (Df) @ 10GHz | Moisture absorption (%) | Application area
|
FR370HR | Isola | 180 | 340 | 3.92 | 0.025 | 0.15 | Normal speed, normal Loss |
FR408HR | Isola | 200 | 360 | 3.63 | 0.0071 | 0.061 | High speed, low loss |
N4000-13 | Nelco | 210 | 350 | 3.6 | 0.009 | 0.1 | Medium speed, low loss |
N4800-20 | Nelco | 180 | 360 | 3.8 | 0.0075 | 0.07 | High speed, low loss |
VT-47 | Ventec | 170 | 340 | 4.27 | 0.016 | 0.12 | Normal speed, normal loss |
VT-901 | Ventec | 250 | 395 | 4.05 | 0.012 | 0.2 | Normal speed, normal loss |
FR4 is hard; even if many electronic components are installed on the printed circuit board, it will not break. Therefore, FR4 is an excellent material for making Rigid PCBs. For flexible circuit boards, there are various flexible materials, such as PI. FR4 can also be used as a reinforcing rib material for flexible circuit boards.
The surface colors of FR-4 are yellow, white, black, and blue.
FR4 Substrates Example
- Iteq: IT180A/IT170GRA1/IT958G/IT968/IT968SE/IT988GSE
- Tuc: Tu 862HF/Tu872LK/Tu872SLK/Tu872SLK-SP/Tu883/Tu933+
- Panasonic: Megtron4/M4S/Megtron6/M6G/M7E/M7NE
- Park Meteorwave series: MW1000/2000/2000/ 3000/4000/8000
- ShengYi: S1000-2(M)/ S7439/S6
- Rogers: RO4003/RO3003/RO4350B (RF material) .etc.
Grades of FR-4

- FR-4 A1 Grade Copper Clad Laminate
Copper plates are mainly used in electronic products such as the military industry, communications, computers, digital circuits, industrial instrumentation, and automotive circuits. The quality of this series of products has completely reached the world-class level. It is the highest-grade and best-performing product.
- FR-4 A2 Grade Copper Clad Laminate
This FR4 copper clad laminate level is mainly used for ordinary computers, instruments, advanced home appliances, and general electronic products. This series of copper-clad laminates are widely used, and the performance index can meet the needs of general industrial electronic products.
FR-4 A2 grade copper-clad laminate has an excellent cost-performance, enabling customers to improve price competitiveness effectively.
- FR-4 A3 Level Copper Clad Laminates
This level of copper-clad laminates is used to develop and produce specifically home appliances, peripheral computer products, and ordinary electronic products (such as toys, calculators, game consoles, etc.). The characteristic of FR-4 A3 copper-clad laminate is that it has a very competitive price on-premise, and the performance meets the requirements.
- FR-4 AB1 Grade Copper Clad Laminate
This grade of sheet material belongs to the low-end material of FR-4 copper-clad laminate. However, various performance indicators can still meet the needs of ordinary home appliances, computers, and general electronic products. The price is the most competitive, and the price/performance ratio is also quite excellent.
- FR-4 AB2 Grade Copper Clad Laminate
This grade of copper-clad laminate belongs to low-end FR4 copper-clad laminate products. However, the performance indicators can still meet the needs of ordinary home appliances, peripheral computer products, and general electronic products. This level of FR-4 copper-clad laminate is only suitable for the production of standard double-sided PCBs. Its price is the most competitive, and the price/performance ratio is better.
- FR-4 AB3 Grade Copper Clad Laminate
This grade of copper-clad laminate is a low-grade copper-clad laminate product. Its performance indicators can meet the needs of ordinary home appliances, peripheral computer products, and general electronic products. This level of FR-4 copper-clad laminate is only suitable for making ordinary Double-sided PCB. Its stability is slightly worse than the AB2 grade board, but the price is low and affordable.
- FR-4 B Grade Copper Clad Laminate
This grade of copper-clad laminate is a secondary product, and its performance indicators can meet the needs of less demanding electronic products. It is only suitable for the production of standard double layer PCB. It has the lowest price.
- FR-4 Halogen-free Copper Clad Laminate
This series of products is the future development trend of copper-clad laminates in terms of environmental protection. They can be used in electronic products such as the military industry, communications, computers, digital circuits, industrial instruments, and automotive circuits. The quality of this grade FR-4 product fully reaches the world-class level.
FR4 Sheet Parameters and Conventional Thickness

FR-4 Sheet Parameter Classification
The critical parameters are Dielectric Constant, Dielectric Loss, and TG Value.
FR-4 sheet is a double-sided copper-clad PCB sheet made of epoxy resin and glass cloth. The relative dielectric constant of the commonly used FR4 copper-clad sheet is 4.2—4.7. This constant dielectric changes with temperature. In the temperature range of 0-70 degrees, the maximum change range of its dielectric constant can reach 20%. The change in the dielectric constant will cause a 10% change in the line delay—the higher the temperature, the greater the delay. The dielectric constant also changes with the signal frequency. The higher the frequency, the smaller the dielectric constant. In general, the classical value of the dielectric constant is 4.4. The constant dielectric changes with frequency as shown in the figure:
The dielectric constant (DK, ε, Er) determines the speed at the electric signal propagates in the medium. The speed of electrical signal propagation is inversely proportional to the square root of the dielectric constant. The lower the dielectric constant, the faster the signal transmission speed. Suppose you are running on the beach. The depth of the water floods your ankles. The denser the water, the slower you run. The viscosity of water is similar to the dielectric constant in the electric medium. The higher the dielectric constant, the slower the electric signal propagates.
The dielectric constant is not very easy to measure or define. It is related to the characteristics of the medium and the test method, test frequency, and the state of the material before and during the test. It also changes with temperature and some unique materials used in the development of the board. Humidity is also an essential factor affecting the dielectric constant because the dielectric constant of water is 70, and very little moisture can cause significant changes.
FR4 sheet dielectric loss is the energy loss caused by the insulating material under the action of an electric field due to the hysteresis effect of dielectric conductivity and dielectric polarization. Under the action of an alternating electric field, the complementary angle δ of the included angle (power factor angle Φ) between the current phasor and the voltage phasor flowing in the dielectric is called the dielectric loss angle. The dielectric loss of the FR4 sheet is generally 0.02, and it will increase with the increase of frequency.
Regular Thickness of FR4 Board
When we order PCB, we need to provide information, such as Gerber, to the PCB manufacturer. In addition, we need to specify the PCB base material, such as FR4 and board thickness. The thickness of FR4 depends on the needs of the project.
How to choose the thickness of FR4?
- Space: If the PCB space is very limited, the PCB should be thin. The thinner the board, the better. This is also the main consideration for us to manufacture more miniaturized electronic products. The smaller the board, the more space in the device is saved.
- Weight: In theory, the thinner the PCB board, the lighter the weight. A thin and small board can reduce the volume of the product, which can contribute to the miniaturization and lightweight of the end product. Smaller and lighter products not only reduce transportation and distribution costs but also reduce the product’s cost that is more attractive to consumers.
- Impedance Matching: The thickness of the FR4 material determines the thickness of the dielectric, which in turn affects the capacitance value of the entire PCB.
- Flexibility: Thinner printed circuit boards can be bent to a certain extent, and sometimes we need to bend the circuit boards. Therefore, the flexibility of the circuit board can be positive or negative, depending on your application requirements. If the product is often stressed or bent, it may be more appropriate for us to choose a flexible circuit board.
- Installation of through-hole components: Not all electronic components can use surface mount technology. The pins of through-hole components are long and short. If the thickness of the FR4 PCB exceeds the pin length of the electronic components, this will have a significant impact on the functionality and compatibility of the circuit board.
Commonly used thickness: 0.3mm, 0.4mm, 0.5mm, 0.6mm, 0.8mm, 1.0mm, 1.2mm, 1.5mm, 1.6mm, 1.8mm, and 2.0mm.
Commonly used copper thickness for FR4 copper clad laminate: 0.5oz, 1oz, and 2oz.
FR-4 Process Technology

In epoxy resin copper-clad laminate production, FR-4 copper clad laminate has always maintained its dominant position.
- FR-4 Resin Glue Liquid
(a) Resin glue liquid formula:
FR-4 copper clad laminate has been produced for many years in the epoxy resin copper clad laminate industry. The resin glue liquid formula is the same.
(b) Preparation Method
- i) Stir and mix dimethylformamide and ethylene glycol methyl ether to prepare a mixed solvent.
- ii) Add dicyandiamide and stir to dissolve.
iii) Add epoxy resin, stir and mix.
- iv) 2-Methyl imidazole is pre-dissolved in an appropriate amount of dimethylformamide and then added to the above materials. Continue to stir thoroughly.
- v) After parking (curing) for 8 hours, take samples and test the relevant technical requirements.
(c) Technical Requirements for Resin Glue Liquid
- i) The solid content should be 65% to 70%.
- ii) Gel time (171°C) 200~
- Bonding Sheet
(a) Manufacturing Process
After the glass fiber cloth is unrolled, it enters the glue tank through the guide roller. After dipping, it passes through the squeezing roller to control the resin content and then enters the oven. During the oven, the solvent and other volatiles are removed, and the resin is in a semi-cured state simultaneously. After leaving the oven, cut according to the size requirements and neatly stack them on the storage rack. Adjust the gap of the squeezing roller to control the resin content. Adjust the temperature, air volume, and speed of each temperature zone of the oven to control the gel time and volatile content.
(b) Testing method
To ensure the quality of the adhesive sheet manufacturing process, various technical requirements must be tested regularly. The detection method is as follows:
- At least 25mm from the edge of the adhesive sheet, cut three samples according to the width direction from the left, middle and right. The sample size should be 100mm×100mm, and the diagonal must be parallel to the latitude and longitude.
- Weigh one by one (W1), accurate to 0.001g.
- Place the sample in a muffle furnace of 524-593, burn for more than 15 minutes, or burn until all carbides are removed.
- Move the sample to a desiccator and cool to room temperature.
- Weigh each piece (W2), Accurate to 0.001g.
- Calculation: Resin content=[(W1-W2)/W1]×100%
How to Make the Final Choice?

In short, FR4 is widely used due to its low cost and good mechanical properties, stability, reliability, etc. As one of the core materials for printed circuit board manufacturing, FR4 also has different specifications, thicknesses, and sizes to choose from, but not every application is very suitable, especially for high-frequency, high-speed, and RF/microwave applications.
FR4 can have various Tg values. There can be low (130-140˚C), medium (150˚C<Tg<170˚C) or high Tg (over 170˚C) PCBs. High Tg PCB can be used in environments with high temperature and thermal stress. It also requires a PCB board with a higher Tg value. Although FR4 also has temperature resistance, when the working temperature of the PCB board is higher than 170°, it is necessary to choose a board with a high Tg value.
Can FR4 be Replaced?
In fact, there are many boards that can be used to replace FR4 as a material for PCB manufacturing, such as FR2/CEM-1 and CEM-3. FR4 has advantages that other plates cannot achieve. Nevertheless, there are other materials that can replace FR4.
What is the Difference Between Glass Fiber Board, Epoxy Board, and FR4 Board?

1) Different Uses
The main raw materials for the production of circuit boards are alkali-free glass cloth, fiber paper, and epoxy resin.
Glass Fiber Board: base material glass fiber cloth
Epoxy Board: the binder is epoxy resin
FR4: base material cotton fiber paper.
All three types are fiberglass boards.
2) Different Colors
Usually, the yellow epoxy board on the market is phenolic epoxy. It is not used as a hard circuit board substrate and for electrical insulation purposes. On the contrary, FR4 is a pure epoxy sheet of NEMA standard. The normal color is dark green, which is the color of epoxy.
3) Difference in Nature
Fiberglass board has the characteristics of sound absorption, sound insulation, heat insulation, environmental protection, and flame retardancy. FR-4 is also known as fiberglass board, fiberglass board, FR4 reinforcement board, FR-4 epoxy resin board, flame-retardant insulation board, epoxy board, FR4 light board, and epoxy glass cloth board.
The IPC - 4101: Rigid and multilayer PCB base material specification
Our commonly used PCB substrates are FR-4, FR-2, CEM-1, CEM-3, etc. What do these professional terms mean? PCB substrates can be classified according to the type of reinforcement material, the type of resin, the flame retardant and the filler used, the glass transition temperature (Tg value) of the resin, and other material properties.
The most frequently referenced international standard for PCB substrates is IPC-4101, the “Specifications for Rigid and Multilayer Printed Board Substrates,” representing the classification and specifications of various materials currently in use.
The IPC-4101 specification for various substrate performance indicators, including Tg, peel strength value under different test conditions, volume resistivity, surface resistance, water absorption, dielectric breakdown voltage, dielectric constant, loss tangent, resistance The bending strength and arc resistance have been stipulated.
Common PCB substrate materials
FR-2 is made of multilayer fiber paper impregnated with flame-retardant phenolic resin. It has good stamping resistance and is relatively low in cost. It is usually used in simple applications, such as radios, calculators, or toys that do not require high dimensional stability and performance. FR-3 is also paper-based, but it is used with impregnated epoxy resin.
CEM-1, the core material is reinforced with wood pulp paper, and the fabric-reinforced is glass fiber cloth, both of which are impregnated with epoxy resin. This material is accessible to stamp and has good electrical and physical properties. CEM-1 has been widely used in consumer products and industrial electronic products.
CEM-3 is different from CEM-1. The core material of CEM-3 is glass fiber paper (non-woven glass cloth) impregnated with epoxy resin, while the fabric is reinforced with glass cloth and impregnated with epoxy resin. CEM-3 is more expensive than CEM-1, but it is more suitable for processing plated holes. CEM-3 has been used in early home computers, automobiles, and home entertainment products.
FR-4 is by far the most commonly used PCB substrate, which is made of glass cloth impregnated with epoxy resin or hybrid epoxy resin. FR-4 substrate has excellent electrical, mechanical, and thermal properties and is widely used in computers and peripherals, servers and storage networks, communications, aerospace, industrial control, and automobiles. It is the ideal substrate.
Related PCB Manufacturing Services
Read More
- Classification Of PCB Materials And How To Choose The Correct PCB Substrate
- Unveil the mystery of high TG PCB circuit boards Materials
- Why choose FR4 as the general material of PCB?
- Why is FR4 Used to Make High Tg PCBs?
- How to Choose the Right PCB Manufacturer and Supplier
- 6 Tips For Looking For A PCB Prototype Manufacturer
- Quick Turn PCB Fabrication And Assembly Services In China
- Complete Introduction of Flexible Circuit Board Materials