Introduction to flexible electronic and materials for manufacturing the flexible PCB
What is a Flexible Circuit Board?
FPC (Flexible Printed Circuit) is a board made of a flexible insulating substrate. Flexible circuit boards can provide good electrical performance and have the characteristics of high assembly density, lightweight, and minimal thickness. They are mainly used in mobile phones, notebook computers, PAD, digital cameras, LCM, and aerospace products.

Classification of FPC - What are the types of flexible electronics?
According to the combination of base material and copper foil, FPC can be divided into:
1) Adhesive Flexible Circuit Board: It means that the copper foil and the substrate are glued together by glue, which is also a standard flexible printed circuit board we use.
2) Non-adhesive Flexible Circuit Board: The combination method differs between adhesive and non-adhesive flexible boards. In non-adhesives flex PCB boards, hot press the copper foil and the substrate together. In comparison, its flexibility, The bonding strength of copper foil and substrate, the flatness of the pad, and other parameters are better than the flexible PCB with glue. However, its price is relatively high, and it is generally only used on high-demand occasions, such as COF (chip on film, bare chip mounted on a flexible board) and so on.
According to the structure, FPC can be divided into:
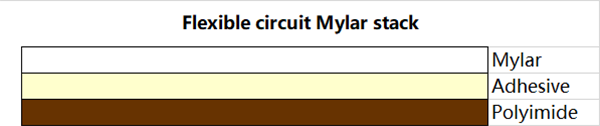
Single-layer flexible circuit board: This is the simple structure of a flexible PCB. Usually, its raw materials include a substrate, transparent glue, copper foil, protective film(Cover lay), etc.
Double-sided Flexible Circuit Board: There are pads on both sides of the double-sided flexible circuit board, mainly used for connection with other circuit boards. Although it is similar to a single-layer flexible circuit board, its manufacturing process differs greatly. Its raw materials are copper foil, cover film, and transparent glue. We have seen and used the double-sided flexible PCB the most.
Double-layer Flexible Circuit Board: When the circuit is too complicated, a single-layer flexible circuit board cannot be wired, or copper foil is required for grounding shielding. In this case, a double-layer or even multilayer circuit board is needed.
Multilayer Flexible Circuit Board: The most typical difference between a multilayer PCB and a single-layer PCB is the addition of a via structure to connect each layer of copper foil. Multiple single-layer boards are connected as a whole through vias to meet the requirements for more circuits.
Features of FPC Products - What are the advantages of flexible circuits?
1) It can be bent freely, folded, and wounded and can be moved and stretched freely in a three-dimensional space.
2) It has good heat dissipation performance, and FPC can be used to reduce the product volume.
3) Offers lightweight, miniaturization, and thinness. For component devices, it is integrated with wires and plays a pivotal role in electronic products.
Manufacturing materials for flexible circuit boards - How to make a flexible PCB?
Three elements of FPC are called flexible circuit board materials.
- Copper Foil
- Adhesive
- Polyimide & Polyester
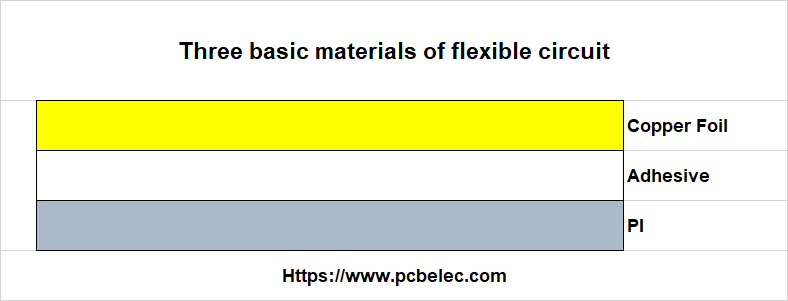
Copper Foil
Copper foil is a conductive layer that covers and adheres to an insulating substrate and forms conductive lines through subsequent selective etching.
Copper foil can be divided into electrolytic copper foil and rolled copper foil.
Rolled copper foil is made by repeatedly rolling a copper plate, and its crystallization is a lamellar structure.
The electrolytic copper foil is continuously produced on the circular cathode drum by a special electrolytic machine. Its structure is a columnar structure.
After the copper foil is produced, it must be surface treated. The contact surface is roughened, the peeling strength is enhanced, and the other surface is treated with oxidation resistance. Therefore, copper foil is divided into the bright surface (copper surface) and processed surface (matte surface).
Copper Foil Thickness
The thickness of the copper foil is used to use “weight” as the value of “thickness”. For example, if 1oz of copper foil (28.35 grams) is spread evenly on an area of 1 square foot, its thickness is exactly 1.37 mils (about 1.4 mils). 1oz=1.4mil, 1 inch=25.4mm, 1 inch=1000mil
The standard thickness of the copper foil is 0.5oz (0.7mil, 18um), 1.0oz (1.4mil, 35um), and 2.0oz (2.8mil, 70um).
Notes:
- The ductility and bending resistance of rolled copper foil are better than that of electrolytic copper foil. The elongation rate of rolled copper foil is 20% — 45%, and the elongation rate of electrolytic copper foil is 4% — 40%.
- When choosing rolled copper, pay attention to the rolling direction of the copper foil. The rolling direction of the copper foil should be consistent with the main bending direction of the circuit board.
- Rolled copper foil is mostly used for flexible circuit substrates, which is more suitable for multiple windings.
Insulation Material
- The insulating substrate for flexible PCB is a flexible insulating film. As the insulating carrier of the circuit board, the choice of flexible dielectric film requires a comprehensive investigation of the heat resistance, thickness, mechanical and electrical properties of the material.
At present, insulating materials for flexible electronics manufacturing are divided into PI(Polyimide) Film, PET(Polyester) Film, and PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) Film.
The price of PI is high, but its flame resistance is good. The price of PET is lower, but it is not heat resistant, so PI is used for welding.
At present, nearly 80% of flex PCB manufacturers use polyimide film materials, and about 20% use polyester film materials for FPC.
The thickness of the insulating materials is 0.5mil, 1.0mil, 2.0mil, 3.0mil and 5.0mil.
PI
- Generally, PI is used as base film (base film in base material and cover film). It has high-temperature resistance characteristics and can be welded, and the electrical and mechanical properties are very great. It is the most commonly used material for FPC manufacturing, and the one with a thickness of 25um is the cheapest. The price of PI increases as its thickness increases.
The conventional thickness of PI is 0.0125-0.125um.
- PI manufacturers mainly include:
- Dupont (America): Kapton has three types of PI films: HN type, FN type, and VN.
- UBE (Japan): UBE has UpilexR, UpilexS, and UpilexC series films with thickness specifications of 25-125um (the Rtype and Ctype have 7 specifications). Compared with Kapton, UpilexS has the characteristics of high heat resistance, better dimensional stability, and low moisture absorption.
- Kaneka (Japan): Apical is produced by Kaneka. The thickness specifications of the polyimide film are 175um, 200um, and 225um. Apical series PI products are mainly used in FPCS, electronic materials, satellites, superconducting facilities, insulating coating materials, etc.
- MGC (Japan): MGC is currently the world’s only manufacturer capable of truly producing transparent PI films industrially. Its PI products can meet the needs of electronic products with high heat resistance and high transparency. The products are mainly used in flexible display-related products and optical components.
- SKCK-OLONP (Republic of Korea): SKC and KOLON turned into a joint venture in June 2008. There are currently IN type, IF type, and IS type PI films.
- Mitsui Chemicals (Japan): Based on its own unique polymer design technology and reaction technology, Mitsui Chemicals has developed a highly heat-resistant and highly transparent PI film with a glass transition temperature of more than 260℃ and a light transmittance of more than 88.0%. The product AURUM™ (thermoplastic polyimide) can be used in precision machinery, automobiles, special wire sheaths, films, fibers, and composite substrates.
- Taimide (Taiwan China): Polyimide film products are produced by Taimide include,
a) Taimide®TH: The film has a thickness between 12.5 μ m-125 μ m.
b) Taimide®TL: The film has a thickness between 12.5μm-50μm. It can be applied to flexible printed circuit boards, cover films, reinforcing materials, composite boards, flexible copper foil substrates, etc.
c) Taimide®TX: The thickness is 7.5μm. It can be applied to the thin high-temperature insulating tape, thin pressure-sensitive tape, and rigid-flex PCB.
d) Taimide®BK: Black polyimide film has a thickness of 10μm-75μm. It can be applied to an opaque high-temperature insulating tape, opaque enhanced version, composite panels, etc.
e) Taimide®OT: Colorless polyimide film with a thickness of 12.5μm-50μm. It can be applied to high temperature resistant colorless protective film, flexible displays, flexible electronics, etc.
f) Taimide®WB: White polyimide film with a thickness of 12.5μm-25μm. It can be applied to a flexible printed circuit board, the high-temperature white cover film, the reinforcing sheet, LED strip, bar code printing, etc.
- The harder the PI in the substrate, the more stable the size. But the harder the PI in the cover film, the worse the coverage.
- For the selection of insulating materials, the following points are mainly considered: mechanical strength, flexibility, dimensional stability, insulation properties, heat resistance, chemical resistance, moisture absorption, and price.
PET
- If used under conditions that do not require high-temperature resistance, polyester film is also a good choice as a flexible circuit board material. The polyester film has moisture absorption and dimensional stability better than PI. The colorless and transparent properties of PET are also not available in PI.
- When the temperature is 60-80 degrees, the mechanical properties of PET will change and decrease.
- The main purpose of PET is still used at room temperature, and the fine-pitch high-density circuit has not been used. It is difficult for the polyester film to reach the UL spontaneous combustion rating.
- PET is generally used as a base film but also plays a reinforcing role in flexible circuit boards.
Comparison of characteristics of FPC insulating material PI and PET | ||
| characteristic | Polyimide(PI) | Polyester(PET) |
| Flexibility resistance | A | A |
| Dimensional stability | C | D |
| Tensile strength | A | A |
| Insulation strength | C | C |
| solderability | A | F |
| Chemical resistance | C | C |
| Thermal expansion | E | E |
| Hygroscopicity | E | E |
| Grade | A=excellent,B=Very Good,C=Good,D=Fair,E=Low,F=Poor | |
PTFE
PTFE (Poly Tetra Fluoro Ethylene) is produced by DuPont under the trademark “Teflon”, so PTFE is often called “Teflon”.
PTFE has excellent comprehensive properties:
- Chemical Inertness: Almost all strong acids, strong bases, strong oxidants, or organic solvents can’t dissolve it, so PTFE is also called “Plastic King”.
- Thermal Stability: The melting point of PTFE is 327℃, the cracking temperature is above 400 ℃, and it can work stably for a long time in the range of -200 ℃ ~ 260 ℃.
- Excellent Electrical Properties: PTFE is the material with the best insulation properties among the known plastics, and its volume resistance is as high as 1018Ω·cm. PTFE is also the material with the best electrical properties among the known materials, its dielectric constant is about 2.1, and its dielectric loss is less than 5×10-4 and is minimally affected by frequency and temperature.
- Flammability: The limiting oxygen index of PTFE is greater than 95%, and the flame retardant grade reaches UL94V-0.
- Non-sticky: The contact angle of PTFE and water is 114°, and almost all viscous substances cannot adhere to PTFE’s surface.
- Good Weather Resistance: PTFE material can be exposed outdoors for more than 20 years without significant loss of mechanical properties.
PTFE is mainly used in the manufacture of flexible copper clad laminates to use its excellent dielectric properties. It is the organic material with the best dielectric properties found so far. The excellent dielectric properties are conducive to completing and speeding up the signal transmission.
The second is to use the high heat resistance and weather resistance of PTFE. These properties ensure that electronic equipment can normally work for a long time in a relatively harsh environment, such as exposure to the outdoors and places with large temperature differences. Therefore, PTFE copper-clad laminate is one of the indispensable materials in the military, aerospace, and aviation fields.
Adhesive of FPC
The role of adhesive is to bond film and metal foil, or bond film and film (cover lay). Different adhesives can be for different film substrates.
The main considerations for choosing adhesive are the fluidity of the material and its thermal expansion coefficient.
Usually, adhesives have two types: Acrylic and Epoxy. Its standard thickness is 0.5mil, 1.0mil, and 2.0mil.
| Comparison of Adhesive Features | |||
| characteristic | Acrylic | Modified Epoxy | Butyral Phenolic |
| Chemical resistance | C | B | A |
| Temperature resistance | A | C | C |
| Electrical property | C | B | A |
| Associativity | A | C | D |
| Flexibility resistance | B | C | A |
| Hygroscopicity | C | B | B |
| Grade | A=Excellent,B=Very Good,C=Good,D=Fair | ||
- The adhesives used in flexible circuit boards mainly include acrylic and epoxy.
- Acrylic adhesives have excellent heat resistance and high bonding strength, but the electrical properties are not ideal, and the insulation resistance is comparable to epoxy resin. The ratio is 1-2 levels worse, and it will cause copper migration under high-temperature environmental conditions.
- Epoxy resin adhesives are lower in heat resistance than acrylic adhesives, but all their properties are relatively balanced and good.
- In the protective film, the acrylic resin has stable fluidity, good fill ability between the line conductors, and convenient operation. But its electrical performance is slightly worse, so try to avoid using it on the substrate with small line spacing and high electrical performance requirements.
- Factors to be considered when choosing glue for flexible circuit board manufacturing are as follows: adhesion, flexibility, chemical resistance, heat resistance, moisture absorption, electrical properties, and price.
- The reaction of epoxy glue is constantly going on, all under certain storage conditions. Even if it is stored in the warehouse, it is also reacting.
- Acrylic acid will only react under certain conditions, so its storage time is relatively long.
- Epoxy glue is relatively strict for pressing conditions. If the pressing conditions are poor, the board will show a big difference. At the same time, the epoxy glue will have performance changes after many times of pressing. The performance of all multilayer PCB using acrylic acid in the production is much better than using epoxy glue. DuPont’s LF0100 is now commonly used in the manufacture of multilayer PCBs.
Types of Base Materials for Flexible Circuit Boards
Flexible substrates are divided into adhesive substrates and non-adhesive substrates, including single-sided substrates and double-sided substrates.
- Glued base material refers to the material formed by laminating copper foil and insulating material with glue.
- Glue-free base material is a material made by directly combining copper foil and insulating material through various special methods.
The processing methods of non-adhesive substrates include electroplating, coating, and pressing.
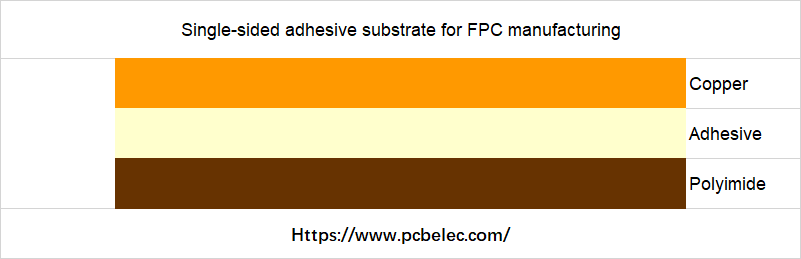

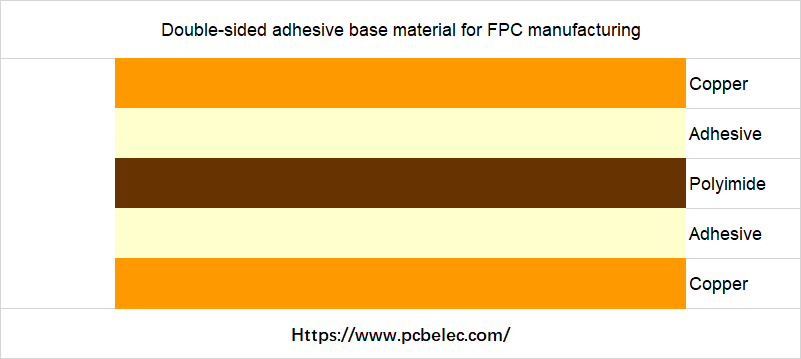
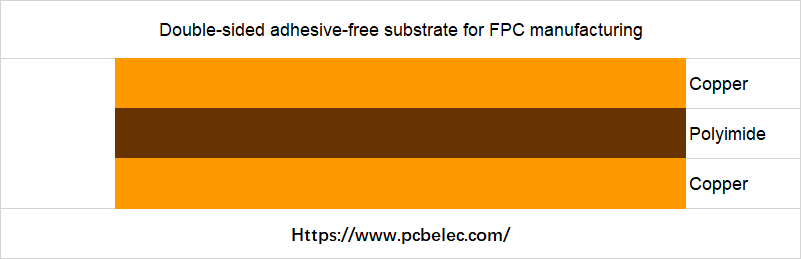
Protective Film (Cover Lay)
The cover layer is an insulating protective layer covering the surface of the flexible circuit board, which plays a role in protecting the conductors on the surface of the flexible circuit board and increasing the strength of the substrate.
There are generally two types of protective materials for the outer layer of the flexible circuit board. The first is the dry film type (cover film), which is polyimide, and it is directly laminated with the circuit board that needs to be protected after etching without an adhesive way of pressing. This kind of cover film needs to be pre-formed before pressing, exposing the part that needs to be welded, so it cannot meet the requirements of finer assembly.
The second type of protective material is the photosensitive development type. The first type of photosensitive development type is to expose the soldering part through the photosensitive development method after the dry cover film is pressed by a laminator, which solves the problem of high-density assembly. The second type is a liquid screen printing type of cover material, and the commonly used ones are Thermosetting polyimide materials and special solder resist inks for photosensitive and developing flexible circuit boards. This material can better meet the requirements of fine-pitch, high-density assembly of flexible circuit boards.
- The protective plastic film has a thickness of 1.4mil, 1.0mil, 0.5mil, and 2.0mil.
- The PI protective film has a thickness of 0.5mil, 1.0mil, 2.0mil, 3.0mil, and 5.0mil.
Note: Some FPC surface layers do not use cover film but use solder resist to control costs.
The Reinforcing Material (Stiffener) - What materials are used as stiffeners for flexible electronics?

Reinforcing material is a hard material added to a local area of the flexible circuit board for the purpose of strengthening the component area and facilitating installation.
There are several types of reinforcement materials as follows
- PI
- PET
- FR4
- Aluminum sheet
- Steel sheet
PI has a higher price, but the flame resistance is good. The price of PET is low, but it is not heat resistant. Thus, use PI / FR4 /Aluminum, stainless steel when welding is required.
Special Instructions:
- Flexible circuit boards that need reflow during assembly need to use PI/FR4/Aluminum/Stainless steel. It must be laminated with thermosetting adhesive or bonded with high-temperature PSA (Pressure sensitive adhesive) 3M966 and 3M9079. In terms of cost and manufacturing process, we give priority to 3M966.
- For those without welding requirements, PET, PI, FR4, Aluminum, and Stainless steel can be used, and PSA can be used for bonding.
In short, choose different reinforcing materials according to different environments and requirements.
Comparison of Stiffener Materials
The main purpose of reinforcing materials: In addition to PET, the other four reinforcing materials can be used to strengthen the lead-bearing chip components. Generally, PET is only used to insert the connector part, and PI reinforcement can also be used in this case. The metal reinforcing material can also play a role in heat dissipation.
| Items | Paper phenolic board | FR4 | PET | PI | Metal board |
| Thickness | 0.6-2.4mm | 0.025-0.25mm | 0.0125-0.125mm | No Special Restrictions | |
| Resistance to floating welding | Yes | Good | No | Good | Good |
| Temperature | 70℃ | 110℃ | 50℃ | 130℃ | 130℃ |
| mechanical strength | High | High | Low | Low | High |
| Thermosetting adhesive | No | Yes | No | yes | Yes |
| Spontaneous combustion | 94v-0 | 94v-0 | No | 94V-0 | 94V-0 |
| Cost | Mid | High | Low | Mid | Mid |
Adhesive for pasting between stiffener material and circuit board
- Commonly used adhesives include PSA and hot adhesives.
- Hot adhesives include Epoxy and Acrylic.
- PSA is an adhesive that can be directly pasted on insulating materials without hot pressing and can be pasted multiple times.
- Thickness: 1.0mil, 2.0mil, 5.0mil
- For metal plates such as stainless steel, its bonding strength is poor, so it must be properly treated before using heat.
When using PSA as an adhesive, be sure to drain the air bubbles. In the subsequent process, if it is high temperature, it may cause blistering to deform the board or wrinkles on the board surface due to the bubbling movement during punching.
Comparison of adhesives for stiffeners
Because PSA has low solvent resistance and creeps resistance, its reliability is poor. For high-reliability products, adhesives with good thermosetting should be used.
| Comparison of adhesive for stiffener | ||
| Items | Pressure-sensitive adhesive | Thermosetting adhesive |
| Thickness | 20-100um | 25-50um |
| Bonding strength | Mid | High |
| Creep characteristics | Low | Good |
| Chemical resistance | Low | High |
| Resistance to floating welding | Good | Good |
| productivity | High | Low |
| Material cost | Low | Low |
| process cost | Low | High |
3M Glue
3M Glue is divided into pressure-sensitive glue, heat-sensitive glue, and conductive glue. Among them, the pressure-sensitive glue is not resistant to high temperatures. After lamination, it is gently rolled to make the glue and the product combined.
The heat-sensitive glue is achieved by the hot pressing/fast pressing adhesive effect.
Conductive adhesive is only used when grounding is required. Glue is divided into 3M200, 3M467, 3M468, 3M9471, 3M9495, 3M68532, etc. The thickness is generally 0.05mm-0.10mm. The ideal temperature of 3M glue while pasting is 15-38℃, not lower than 10℃.
Conductive glue can be divided into:
1) Conductive Silver Paste: It is a conductive substance mixed with silver powder and petroleum jelly in a particular proportion to increase conductivity and reduce conductive contact resistance without heating. It is generally used for connection joints of electrical equipment (paint a little conductive silver paste) to increase the conductivity.
2) Different Side Conductive Adhesive: These, such as ACA and ACP, have short heat pressing time, low temperature, high viscosity strength, good reliability, and strong applicability. They make it easier to automate the production line. It is a new type of electronic component circuit board assembly material. As long as it is composed of polyol compound, polyisocyanate, chain extender, epoxy resin, phenolic resin, coupling agent, antioxidant, conductive particles, and solvent, it is made by combining chemical reaction methods physical mixing method.
Characteristics of Conductive Adhesive
1) Lower curing temperature, suitable for heat-sensitive materials and non-weldable materials.
2) It can provide more acceptable spacing, especially anisotropic conductive electronic adhesives, which can be used with a spacing of only 200um. The increasingly dense and miniaturized electronic assembly industry has broad application prospects.
3) The process can be simplified (for wave soldering, the process steps can be reduced).
4) The maintenance performance is good. For the thermoplastic conductive electronic adhesive, the components can be easily replaced after local heating. For the thermosetting conductive electronic adhesive, components can be replaced only by local heating above Ts. Even if the electronic adhesive is fully cured, there is no need to use chemical solvents or sharp tools to remove the residue. You can directly apply a new electronic adhesive and then heat and cure it.
Release Paper
Avoid 3M glue sticking to foreign matter, which is convenient for operation.
Solder Resist Ink
Photosensitive ink (divided into bright oil and matte oil) coats the copper foil and base material on the surface of the flexible circuit board that does not need to be electroplated with solder resist ink, with a thickness of 10μm-20μm.
Flexible PCB Material Suppliers
In addition to the sophisticated manufacturing process required for high-quality printed circuit boards, materials also determine product quality and stability. The commonly used material of Rigid PCB is FR4. Of course, according to different needs and usage scenarios, different materials can also be selected. For example, high-frequency circuit boards need high-frequency materials, and Aluminum PCB’s substrate material is aluminum. The following are well-known flexible circuit board material manufacturers worldwide.
1) DuPont, USA
DuPont was established in 1802 and has made outstanding contributions to developing and researching printed circuit board materials. They provide high-reliability manufacturing materials for various PCB types, such as rigid PCB, single-sided PCB, double-sided PCB, flexible PCB, and rigid-flex PCB.
DuPont’s flexible circuit board manufacturing materials include flexible PCB laminates, dry film photoresists, films, etc.
2) Shengyi Technology
Founded in 1985, Shengyi Technology is a global core supplier of electronic circuit substrates integrating R&D, production, sales, and service. It provides comprehensive and excellent electronic circuit substrate solutions.
Shengyi Technology can provide flexible copper-clad laminate, Coverlay, No-flow prepreg, Stiffener, Bonding film, PET laminated busbar, and other flexible PCB manufacturing materials.
Click here to learn more about flexible materials introduction, or click here to download the list of Shengyi Technology’s flexible materials products.
3) KB-Kingboard
KingBoard Holding Limited established its first copper-clad laminate factory in Shenzhen in 1988. It has more than 60 branch factories and is the world’s largest manufacturer of laminates. The business scope has developed from copper-clad laminates to the production of printed circuit boards and other fields.
Website: http://www.kingboard.com/
4) ITEQ
ITEQ was established in1997 and is one of the printed circuit board base material suppliers located in Taiwan, China. The products mainly include high-end copper foil substrates, films, multi-laminated substrates, heat dissipation materials, high Tg, and unique high-frequency materials. Flexible materials include Flexible Copper Clad Laminate (FCCL), cover lay, Bonding Sheet, Stiffener, etc. FCCL includes Halogen Free FCCL and Normal FCCL.
For the introduction of flexible materials produced by ITEQ, please click here.
Performance characteristics of well-known flexible circuit board materials for download
Roger FPC Materials
- TSE-EMC Shielding Characteristics [100~2000 MHz]
- KEC-EMC Shielding Characteristics [0.2~1000 MHz]
- SF_PC5500_Excellent nonflammable Halogen-free EMI Shielding Film for FPC
- SF_PC5000 Electromagnetic Noise Shielding Film for FPC Applications
- SF_PC1000_Electromagnetic Noise Shielding Film for FPC Applications
NIKAFLEX Materials for Flexible Printed Wiring Boards
Polymide Film Base Copper Clad Laminate for Flexible Printed Circuits
Coverlay Film for Flexible Printed Wiring Boards-Halogen free polyimide film base coverlay.
Summary
High-cost raw materials are the main reason for the high price of flexible circuits. The price of raw materials varies greatly. The cost of the raw materials used in the lowest-cost polyester flexible circuit is 1.5 times of the raw materials used in the rigid circuit. The high-performance polyimide flexible circuit is 4 times or higher. At the same time, the material’s flexibility makes it challenging to automate processing during the manufacturing process, resulting in a decrease in output. Defects are prone to occur in the final assembly process, such as peeling off flexible accessories and breaking lines. This type of situation is more likely to occur when the design is not suitable for the application.
Under high stresses caused by bending or forming, it is often necessary to select reinforcing materials. Although the raw material cost is high and the manufacturing is troublesome, the foldable, bendable, and multilayer jigsaw function will reduce the overall assembly size, reduce the materials used, and reduce the total assembly cost.
The flexible circuit industry is undergoing small but rapid development. The polymer thick film method is an efficient and low-cost production process. This process selectively screen-prints conductive polymer inks on inexpensive, flexible substrates. Its representative flexible substrate is PET. Polymer thick film conductors include silk-screened metal fillers or carbon powder fillers. The polymer thick film method is immaculate, uses lead-free SMT adhesive, and does not need to be etched. Because of its additive technology and low substrate cost, the polymer thick film circuit is 1/10 of the copper polyimide film circuit price. It is 1/2 to 1/3 of the price of the rigid circuit board. The polymer thick film method is particularly suitable for the control panel of the device. In mobile phones and other portable products, the polymer thick film method is suitable for converting components, switches, and lighting devices on the printed circuit board into a polymer thick film method circuit. It not only saves costs but also reduces energy consumption.
Generally speaking, flexible circuits are more challenging to manufacture than rigid ones, and the cost is higher. When manufacturing flexible boards, we have to face the fact that many parameters are outside the tolerance range in many cases. The difficulty in manufacturing flexible circuits lies in the flexibility of the materials.
Although the manufacturing cost of FPC circuit boards is relatively high, the assembly price of flexible circuit boards is declining, becoming close to traditional rigid PCBs.
In the next few years, FPCs (flexible circuit boards) that are smaller, more complex, and more expensive to assemble will require more novel assembly methods, and hybrid flexible circuits will need to be added. The challenge for the flexible circuit industry is to use its technological advantages to keep pace with computers, remote communications, consumer demand, and active markets. In addition, flexible circuits will play an essential role in the lead-free operation.
Related PCB Manufacturing Services
Related Posts
- Knowledge of Plating on Flexible Circuit Board Surface
- Knowledge of Flexible Printed Circuit Board Processing Technology
- The terms you have to know related to the manufacture of Flexible PCB
- What is a Multilayer PCB and What are the Advantages?
- Key Process Flow of Rigid-Fled PCB Production
- Find Out Now, What Should You Do For Fast PCB Classification?
- Single-layer PCB vs. Double-sided PCB: How to Choose?
- PCB Material Types-Circuit Board Materials-How to Choose?
- Why is FR4 Used to Make High Tg PCBs?
- Why choose FR4 as the general material of PCB?
- Unveil the mystery of high TG PCB circuit boards Materials