Table of Contents
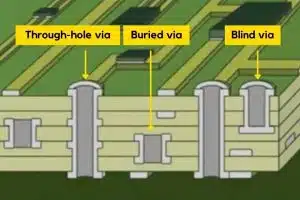
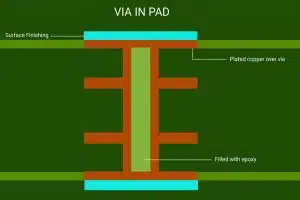
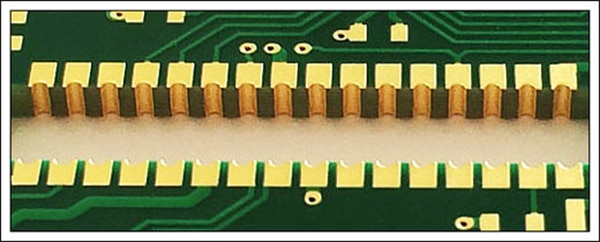
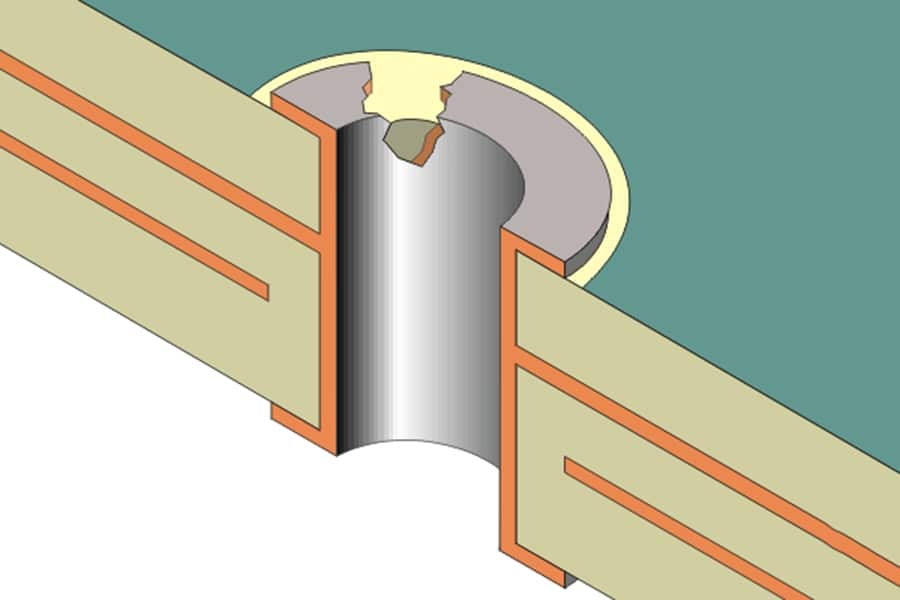
Plated half-holes, also known as castellated holes, resemble plated through-holes in structure but occupy only half the vertical space. As illustrated below, they plate the walls on one side of the hole. Half-holes connect individual PCB modules to main boards via soldering. Compared to under-module pads, they improve joint access and coaxial alignment. Half-holes also facilitate modular board assembly and high-density interconnects.
Design Guidelines
When designing plated half-holes, consider following factors:
- Position precisely on board edges for easy accessibility
- Define as plated through-holes in EDA tools
- Include in drill files for manufacturer
- Add pads on each layer for stability
- Mind minimum sizing based on board thickness
Choose half-hole diameters balancing considerations like via reliability, routing spaces, and costs.
Fabrication Process
Traditional processes have limitations in productivity and performance. Newer methods utilize specialized drilling on panel edges and direct copper plating to boost efficiency. One-step solutions like precision laser cutting also exist.
Benefits
Half-holes simplify soldering, measurement, and inspection versus bottom-located pads. Their edge positioning enhances coaxiality while avoiding dust traps. Half-holes also reduce via filler challenges and enable flexible routing options.
Applications
- Modular boards
- Changing component layouts
- High-density interconnections
- Validating solder joint quality
- Bridging rigid-flex PCB sections
Plated half-holes continue finding increased applications in complex modular PCB designs due to their flexibility and reliability.
Conclusion
Incorporating plated half-holes in suitable designs allows improving interconnect accessibility, manufacturability, and reliability. We hope this overview aids your learning. Please reach out with any questions!