PCB has completely changed the electronics industry and products. You might have seen boards with printed circuits. These boards go through various processes, and then we get the final ready-to-use product. The product is known as the PCB assembly, and the process is called the PCB assembly process.
It is important for a designer, buyer, or beginner to know about the PCB assembly and its complete process and types. Here, we will have a look at these things and explain everything step-by-step. Let’s get into it.
PCB Assembly Process Tutorial
What Do You Mean by PCB Assembly?

PCB assembly is the configuration of a PCB with electronic components on it and soldering components to make the connections solid and stick them to the board.
Recommended reading
You might have seen a bare board without any components and traces. When electrical connections are made on the board, it is called Printed Circuit Board or PCB. After that, components are placed and soldered on the PCB, and a final product is created, which is known as PCB assembly.
There are three types of PCB assemblies: SMT, THT, and Mixed technology. The process of making different types of assemblies is not entirely different; there are minimal changes. When components are placed on the PCB, then there are different methods of soldering them onto the board. The type of soldering depends on the design of the PCB and assembly type, which we will discuss later in this article.
Related Reading: What is the difference between wave soldering and reflow soldering?
First, the circuit is designed, and then the components are placed on it accordingly. The components that are placed on the PCB are capacitors, transformers, resistors, ICs, and other small circuit components. After the assembly, PCB has to go through a series of tests to qualify for approval, and then it is delivered to the customer.
There is a complete process involved in creating a PCB assembly. Moreover, before going to those processes, there are a few things that need to be done in advance. We will explain all these things to give you a clear idea of how PCB assemblies are made.
Types of PCB Assembly
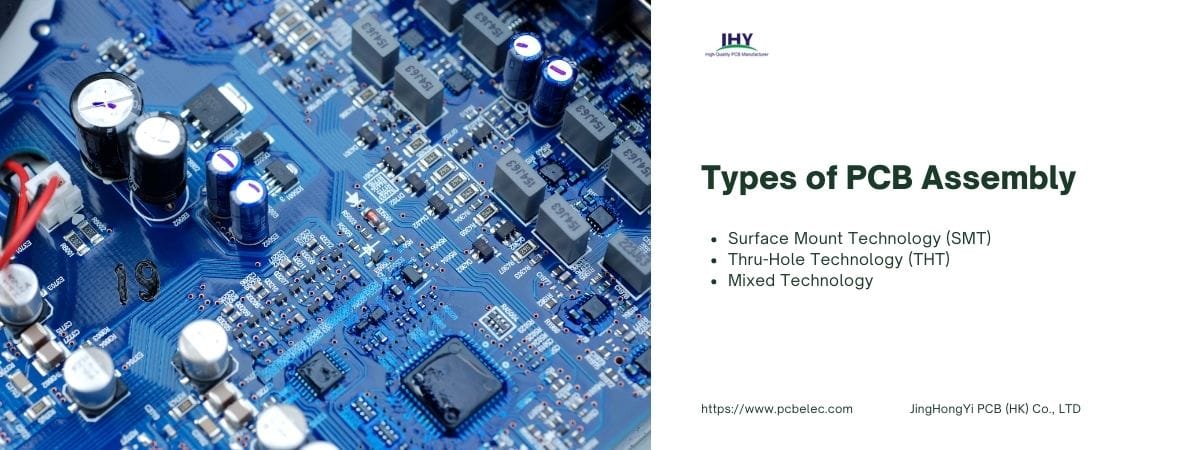
We now know the importance of PCB in the modern technological world. It is used in every electronic device, whether it be computers, digital devices, military, or smartphones. PCB has taken over the world with the ease of circuit. Electrical and electronic components cannot work without it.
There are three types of PCB Assembly, namely SMT, THT, and Mixed technology. Let us see the difference between the assembly types.
1. Surface Mount Technology
Surface mount technology, as the name suggests, means to mount components on the bare board through solder paste. The main difference between THT and SMT is in placing the components on the board. THT uses leads to place the components on the board. SMT is the newer method for PCB Assembly and has a better outcome along with higher efficiency.
SMT uses simple processes of printing solder paste, mounting components, reflow soldering, AOI, and AXI. AOI is automated optical inspection, and AXI means automated X-Ray inspection. These are the quality assurance methods to check the assembly of PCB. SMT has replaced the THT assembly with welding technology.
SMT has many advantages when compared to THT. It is small in size and is usually light in weight because there are no leads in it. It is accessible to smaller PCBs because it takes less surface area and can hold multiple components with efficiency. Precise machines are used to minimize the errors, ensure reliability and consistency of PCB.
SMT enables the PCB to have a compact design with better performance. It reduces the manufacturing time as there is no need for drill holes. It also reduces the cost of labor due to automated machines, uses fewer materials than THT, uses high-density components, and has a better performance than the conventional PCB Assembly method.

Thru-Hole Technology
Thru-Hole Technology or THT is the oldest method of PCB Assembly. In this method, the components are mounted on the board with the help of leads. These leads are inserted into the drill holes, and then the leads are soldered using manual soldering or wave soldering. As we need to drill holes in THT, it is not suitable to perform on double or multi-layer PCBs. It is very difficult to drill holes in a multi-layer PCB and maintain its design and accuracy.
Modern technology and appliances now use and require SMT, and SMT has replaced it in various applications. But THT can never be eliminated; it is because certain applications require THT and are still replaceable. For example, if there is a simple task to perform like a digital clock or a simple toy, why would anyone use SMT when it can be done using THT. This is the reason THT is still used today in different applications and circuits.
THT has some advantages over SMT. It includes the ease of replacing and adjusting the position of components. Moreover, THT is highly used when it comes to PCB testing and prototyping. It has high durability. It has more heat resistance and stress tolerance than SMT and also has better mechanical strength. But sadly, THT has lower efficiency than SMT and has limited or restricted PCB designs.
Type of Soldering
We know that THT assembly requires soldering because it uses leads to mount the component on the bare board. The leads are on the lower surface of the board that needs soldering. Manual soldering and wave soldering are used for soldering these leads and making connections so that circuit can function properly. Let us see what these soldering methods are and what makes them different from each other.
1- Manual Soldering
It is the conventional and oldest method of soldering. Here, a single person is responsible for putting a component, mainly PTH components, into a specific and designated hole and soldering it. Then the PCB is moved to another station where another person is responsible for putting a PTH component in the hole and soldering it. It is a lengthy process and consumes a lot of time. This is the reason it is very less likely to be used in industries with high production requirements. However, some components still need manual soldering.
2- Wave Soldering
Wave soldering is a modern method of soldering, and it has replaced conventional manual soldering. Here, the person only needs to place the components in PTH holes, but it can also be done by a machine. After placing the components, the board is then put on a conveyor, where it is led to a hot oven where the solder melts. PCB goes through a wash of molten solder waves on the lower surface. This wash solders all the pins from beneath. However, wave soldering cannot be applied to a double-sided PCB. If it is applied, then all the electronic components on the lower side will not work. It is why manual soldering is not obsolete and still being used in the industry.
Mixed Technology
As technology is advancing day by day, PCB is also evolving. We see a few PCBs that include a single type of component. Due to this reason, some PCB requires a mixture of SMT and THT.
Mixed technology uses both assembly methods to make a fully functional PCB. Sometimes, it has a one-side SMT and one-side THT. It all depends on the requirements of the customer.
Mixed technology is used where there is a need. It is widely used in complex and complicated circuits. Some appliances require Double-sided mixed assembly, which is only possible in mixed technology. It is simply a combination of both the PCB assembly types.
Preparation Before Assembly Process

PCB design is usually made on software. The design before the assembly is very important because it allows manufacturers to perform a DFM check on the design file.
With the help of simulation, we can check the functionality of the design and what errors it may go through. DFM check also allows us to look for some errors that may arise during the operation or function of the PCB.
Design is made based on the requirement and functionality of the PCB. If the design is incorrect, it can lead to many problems during the assembly and tests after assembly.
Usually, designers make the design according to their requirements. They do not know much about the manufacturing process and requirements. Therefore, a DFM check from the manufacturer is essential to ensure there is no flaw in the design and everything can proceed smoothly.
If any error arises during the DFM check, then it can be rectified easily rather than rectification after the assembly process. The PCB can be designed again, and it will save a lot of cost for the consumer.
The DFM check includes a Power and Ground check, Silkscreen check, Solder Mask check, Drill check, Signal check, and Mixed Layer check. These tests allow the manufacturer to ensure the proper designing and working of the PCB. If a PCB clears all these tests, then it can be assembled as there is no error in the design and the simulation is working perfectly. These tests include several smaller tests that conclude a single test. No test is less important than any other, and all PCB companies must carry out these tests to reduce cost and time and increase the efficiency of PCB manufacturing.
PCB Assembly Process

The PCB assembly process involves various complex stages to create the final assembly. It requires high precision and maximum attention. You need industrial-grade machines to perform certain operations and steps. With the advancement in technology, advanced machines automate the whole assembly process, and the PCB gets ready quicker than ever.
Let us see how a professional PCB assembly company assembles a PCB and what steps a PCB goes through to be fully ready for use along with full functionality.
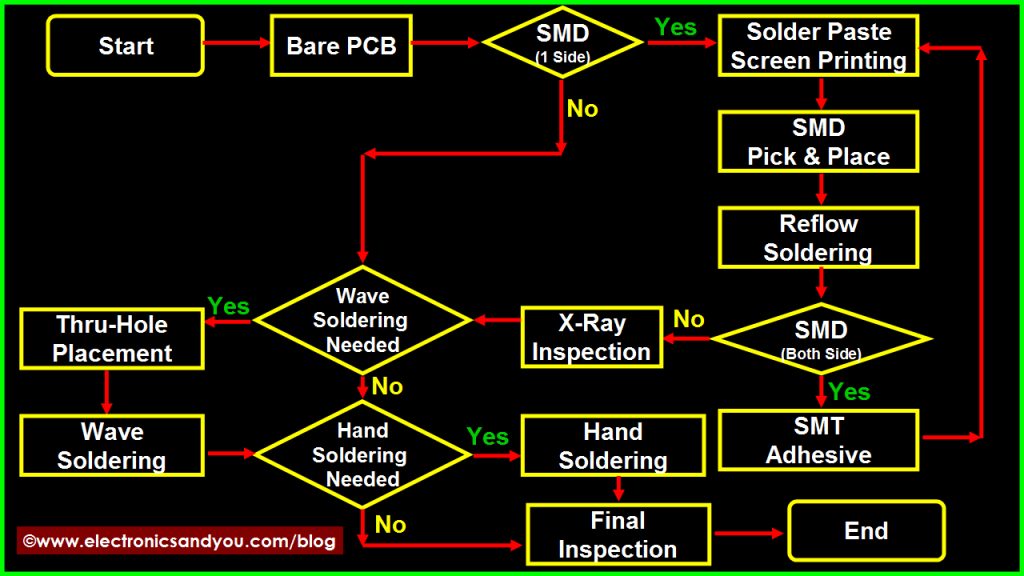
Step 1: Laser Stencil Cutting for Screen Printing
When you need to solder SMD components, a solder paste is applied to the board. The paste is only applied to the places where the components will be soldered in the future, and the remaining part of the board remains as it is. For this, there is a stencil needed to apply the solder paste at suitable parts of the PCB.
Stencils are usually made from stainless steel by the method of laser cutting. The aperture of stencils is designed to make sure and follow the pattern and location of the pads on the PCB. It is very important to obtain the perfect apertures and thickness of the stencil to ensure the correct volume of solder paste. The specific amount of solder paste is then applied to the board to obtain the desired quality of the soldered joint.

Step 2: Solder Paste Application
Solder paste is solder alloy with a combination of flux and other additives. Flux protects contact surfaces from oxidation and has other properties to ensure that the components stay in place before the soldering process.
Solder paste is applied to the surface of the pads by automatic screen printers. These printers are precise and ensure the alignment of the stencil with the board. The paste is then pressed with the help of a special squeegee through apertures of the stencil on the contact pads of the PCB.
The quality of application of soldering paste is controlled by a 3D optical machine that not only checks the volume of the solder paste but also checks the accuracy of solder paste on the PCB contact pads. With the help of this 3D optical machine, other defects are checked as well.
Some manufacturers also use the manual process of applying solder paste on the board. The stencil is placed over the board, and the paste is applied by a worker.
Step 3: SMD Pick and Place
Pick and Place is also automated. It is done by a machine that places the components in the right places. It makes the process faster and helps in turning out more PCBs per day.
The components are arranged on the PCB following the design documentation using a pre-written program. The Pick and Place machines determine the coordinates of reference marks on the panel for correct positioning on PCB contact pads using a high-quality camera. Then, the machine picks the component and places it over the board.
Step 4: Reflow Soldering
After placing components on the board, PCB is then placed on the conveyor to the convection reflow solder oven. These ovens have 6-14 zones of different temperature controls. They are used for smooth and uniform heating and cooling of PCB. All of these ovens are capable of soldering with leaded and lead-free technologies.
When the PCB enters the oven, the solder paste that was applied in the first place melts down, and the components are soldered to the board. A suitable temperature that does not harm the board and components is applied. Once the components are perfectly soldered, the board is cooled down.
Step 5: Optical Inspection
After reflow soldering, the assembly is ready; however, it is necessary to check for errors and issues.
Optical inspection controls the product quality after soldering. This single step of PCB assembly is capable of detecting various issues, including the absence of components, deviation of component positioning, polarity, bridging between leads, and coplanarity.
The machine examines the board and components using cameras. The cameras are positioned at different angles to take the images and compare them with the requirements. Keep in mind that this inspection cannot check the soldering done under the components. In the case of BGA PCBs, the optical inspection cannot check the soldering under the component. Similarly, if there are issues in the layers of the PCB, this inspection cannot find them. However, these issues will be dealt with in the upcoming steps.
AOI evaluates the quality of soldered connections, height and width of the solder fillet, and compliance with local and IPC standards. If any defects are found, these boards are arranged in a separate magazine of the automatic loader and passed to the operators.
Each PCB has its barcode depending on the design and requirement of the client. When you scan the barcode of the PCB, inspection results are displayed on the screen to the operator. The operator or controller then checks and evaluates the quality of soldered connections. If any defect is found, PCB is then moved to a reworking station.
Step 6: tatistical Process Control
In the production process, the product’s quality in the industry is maintained by statistical process control. Quality data is collected and analyzed by software that enables the process engineers to improve the current production process. The system then stores and analyzes different data, including product characteristics that comprise images, 3D models, and measurement results.
A link function is used to compare AOI and SPI data to compare and conduct parallel analysis to identify and eliminate the causes of defects.
Step 7: X-Ray Inspection
The quality of soldered components, including BGA, LGA, CSP, or bottom components, cannot be determined with optical systems. This is the reason we need an X-Ray inspection to further ensure the quality and assembly of the PCB.
PCB with these bottom components is checked with X-Ray machines. X-Ray allows us to control the standard parameters of soldering quality and evaluate the number of voids. It also checks the integrity of internal PCB conductors and components. The rays penetrate the PCB and find all possible issues and faults. If it’s necessary, you can take high-quality images of X-Ray inspection as well.
Step 8: Selective Soldering
After SMD component assembly, THT components are installed on the PCB. Then, the components are soldered automatically.
If this type of soldering is compared with reflow soldering, not all of the components come in contact with the solder. Only the parts of PCB that are directly subject to soldering are soldered. This selective soldering allows high-quality assembly of the complex double-sided board with high component density.
A drop jet fluxing device moves under the lower surface of PCB and applies flux only where necessary. This type of soldering takes place in an inert nitrogen environment that improves the quality of the process significantly.
Some components or devices are also soldered manually by workers. There can be transformers and other devices.
Step 9: Finished PCB Handling
Finished electronic modules pass through the final quality control stage. The operator then performs visual quality control of each module using inspection equipment that involves stereo microscopes. These modules are then packed into anti-static films and sent to the customer or client.
Step 10: Feedback
This step is not followed by everyone in the industry. This is an improvement step that the company wants. When customers are delivered their respective PCBs, they are then asked for feedback after the usage. If customers face any issue, they complain to the company, and then the matter is taken into consideration for the future. In this way, feedback is an important part of industrial growth and improvement.
What to Do After PCB Assembly?

After PCB Assembly, we need to make sure that PCB is fully functional and is performing all the operations as expected. Secondly, we need to make sure that PCB is presentable to the client. In most of the cases of SMT Assembly, the soldering paste leaves flux behind due to human handling.
Dust and dirt may also appear on it, and it does not look good and can affect the functionality of the PCB. This flux on the board becomes sticky after some time and may become acidic that may affect the solder joints of the board. To avoid this issue, we can wash the PCB properly and make sure that it is clean and ready to be delivered to the customer.
When it comes to washing an electrical circuit or a PCB, we require a high-pressure washer. To wash the PCB, we need deionized water, not regular tap water. It is because the ions in tap water will adhere to the circuit and make it problematic. So, deionized water is the best to remove any residues on the board. When the PCB is washed, you can use high compress air to dry it out in seconds. Now, the PCB is ready to be packed and delivered to the customer.
JHYPCB PCB Assembly Services
JHYPCB provides all PCB services under one roof. We are capable of dealing with low-high volume orders and can make almost all types of PCBs. We provide turnkey assembly services, prototype services, stencils, and every service you need.
The state-of-the-art facility and modern equipment ensure high-quality PCB. We are certified by RoHS, UL, and ISO to meet the quality and safety standards. We strive to offer the best services at a reasonable cost.
We deal with complete PCB solutions. We can help you create PCBs from scratch and deliver the final assembly. Everything, including materials and components, is our responsibility, and you will get the ready-to-use product within a few days. For more information and details, feel free to contact our customer support team.
PCB Assembly Process Videos
Printed Circuit Board Assembly Process
SMT PCB Assembly Process | Surface Mount Technology Manufacturing Process
PCB Assembly Factory Tour (Full) – How To Assemble A PCB